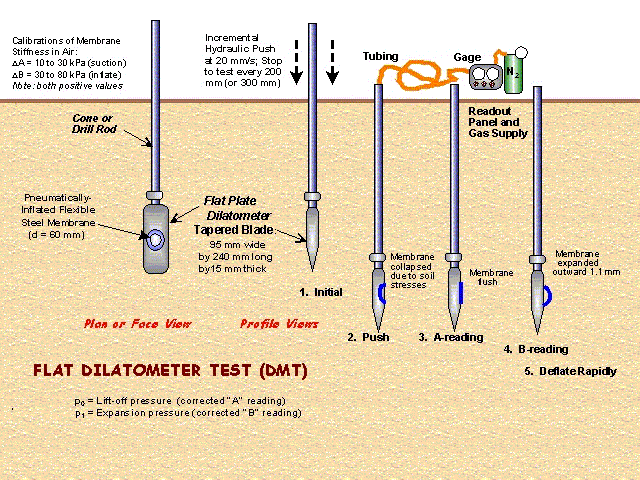
DMT (Flat Dilatometer)
A Flat Dilatometer probe consists in a steel blade with a circular membrane in
one of its sides. The membrane has electrical sensors which can detect its position
(flexed to the inside or outside and parallel to the blade).This blade is pushed into the
ground and at desired depths the membrane is inflated using any kind of compressed gas,
normally nitrogen.
When the probe is pushed into the ground the soil pressure makes the membrane flex
to the inside of the dilatometer blade. At measurement depths the membrane is inflated and
an "A" reading of pressure is obtained when the membrane reaches its initial
position (parallel to the blade), and a "B" reading is obtained when the
membrane displaces 1.1 mm to the outside.
This parameters are used in several correlations to obtain properties of the soil,
such as compressibility and soil behavor classification.
The following graph depicts a normal flat dilatometer sounding.

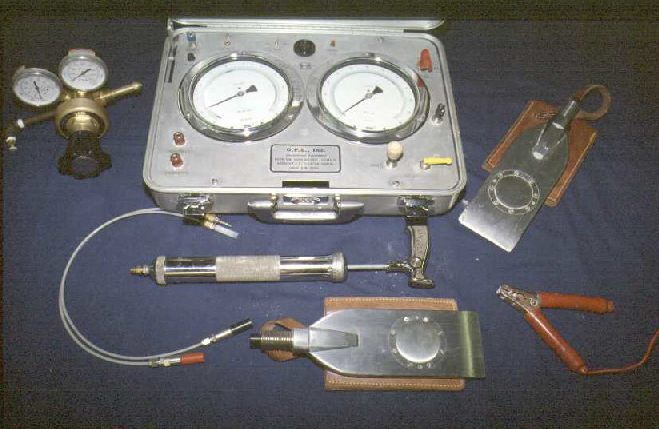
The following picture shows the DMT equipment at Georgia Tech.
